Information and communication technology (ICT) refers to technology that is used to collecting, storing, transmitting and processing data and information. This technology includes notebooks, smartphones, tablets, televisions, and networks.
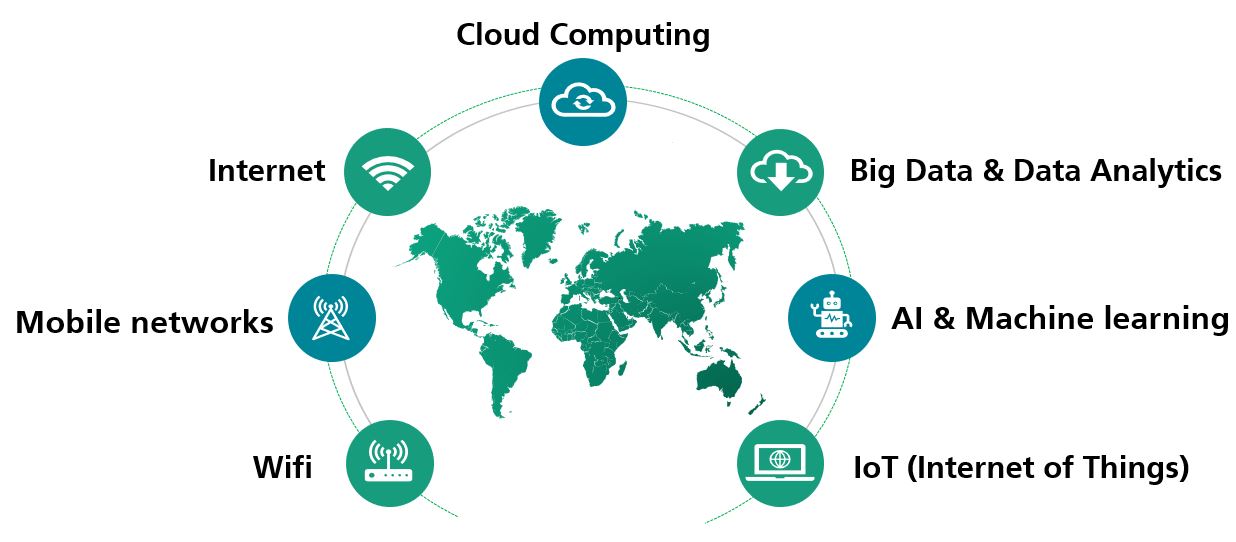
What does ICT include?
- Internet: The Internet is the basis for many other ICT technologies and enables access to information, communication, online services, entertainment and much more.
- Mobile networks: Mobile networks such as 4G and 5G enable wireless communication via cell phones, smartphones and other mobile devices.
- Wireless networks (WLAN): WLAN technology enables wireless connections between devices and the Internet, which increases flexibility and mobility.
- Cloud computing: Cloud computing technologies enable access to computing resources and services via the Internet without them having to be available locally on the device.
- Big data and data analytics: These technologies enable the collection, storage and analysis of large amounts of data in order to gain valuable insights and trends.
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning: These technologies enable computers to perform complex tasks, recognize patterns and make decisions without being explicitly programmed.
- IoT (Internet of Things): IoT comprises networked devices and sensors that can communicate with each other and with the internet in order to collect, transmit and process data.
Everyday examples of ICT use
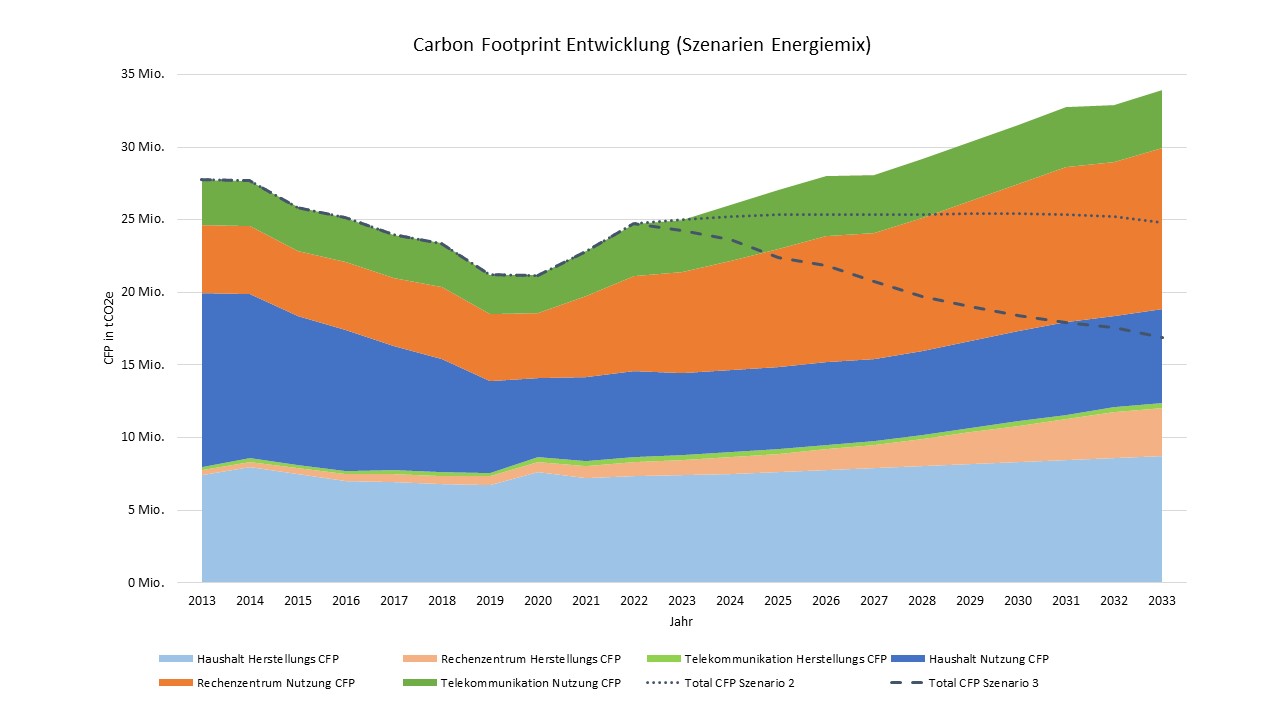
Why is ICT relevant for the environment?
Environmental impacts do not arise "in the product" but during the manufacture of components, through:
- Use of high energy with harmful emissions
- Use of environmentally harmful chemicals
- Use of scarce and environmentally critical raw materials
Semiconductor components are particularly harmful in production. These include "ICs" or "chips" manufactured in clean rooms. These components can account for over 50 % of the manufacturing costs of a cell phone.
How harmful to the environment is chip production currently1?
The smaller the structure size, the higher the power requirement per wafer during production:
- 28 nm chip: approx. 400 kWh
- < 10 nm chip: up to 1200 kWh
Emissions in the semiconductor industry worldwide:
176 million tons of CO2 equivalent in 2022 (this corresponds approximately to the total emissions of the Netherlands)
Daily water consumption of a semiconductor factory:
- Up to 99 million liters (demand of 220,000 German four-person households), 75% of which for production processes
- Up to 50 million liters of ultrapure water (UPW). 1.5 liters of tap water is required per liter of UPW.
- 20 million liters for cooling and air filtration
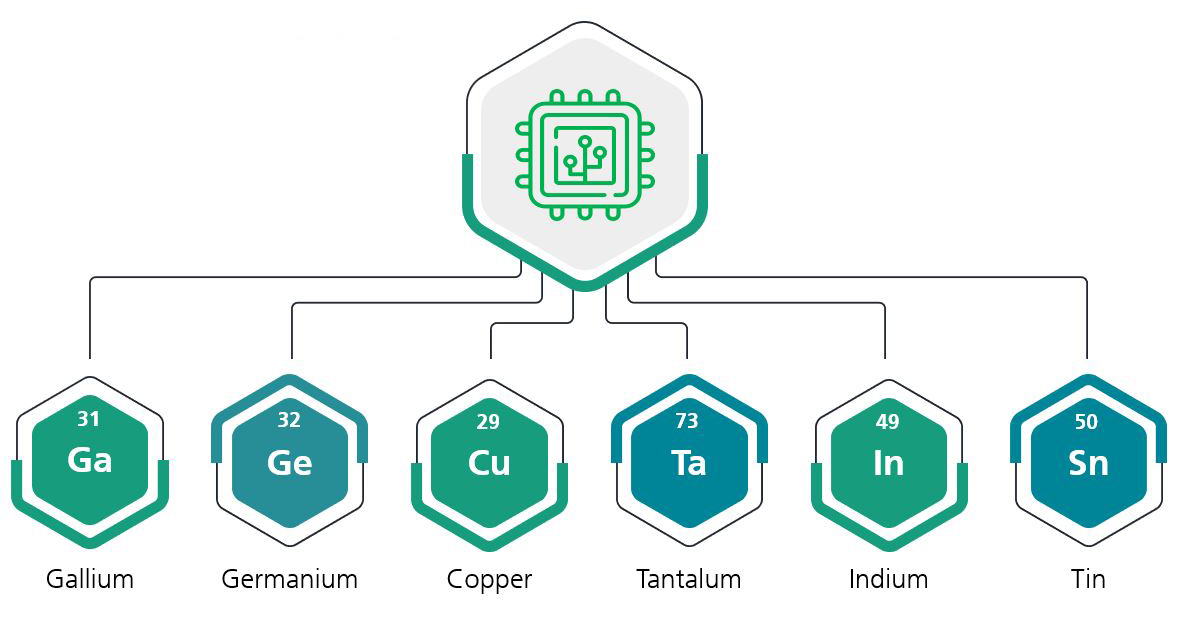
What raw materials are in ICT?
Various raw materials are used in information and communication technologies. Some of these are:
The problem: These raw materials are often mined under dangerous conditions in countries without appropriate social and environmental standards and are sometimes difficult to obtain.
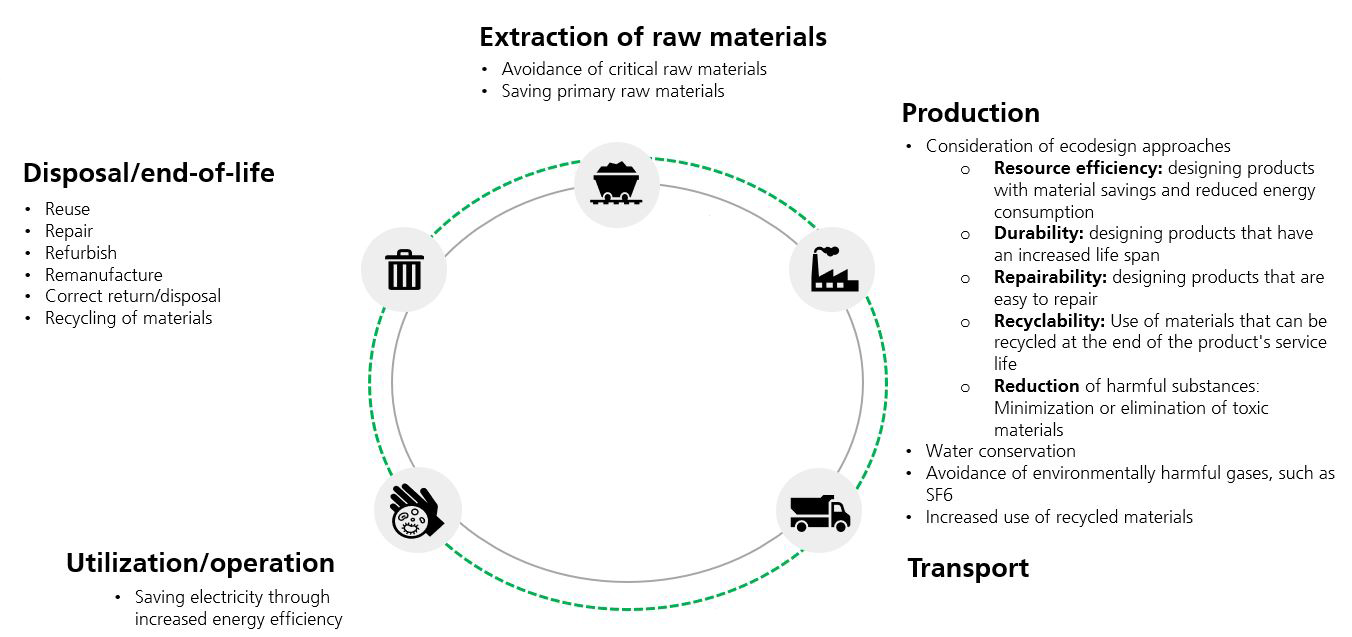
How can ICT be made greener?
Green ICT encompasses a variety of approaches that deal with different aspects of the ICT life cycle:
- Reduction of energy consumption in use
- Reduction of energy and material consumption in production
- Reduction of harmful substances in products and manufacturing processes
- Recycling to recover raw materials
- Sustainable product design and manufacture of hardware that is as durable as possible
- Resource-saving software programming (green software engineering)
- Use of IT to reduce the energy consumption of another source (e.g. traffic, heating systems)
What can I do myself?
- For example, buying used electronics! Purchasing refurbished products saves resources and is also cheaper.
- Keep your cell phone longer. A cell phone usage period of 5 years including a battery change already reduces the annual emissions of a cell phone by as much as 31%2!
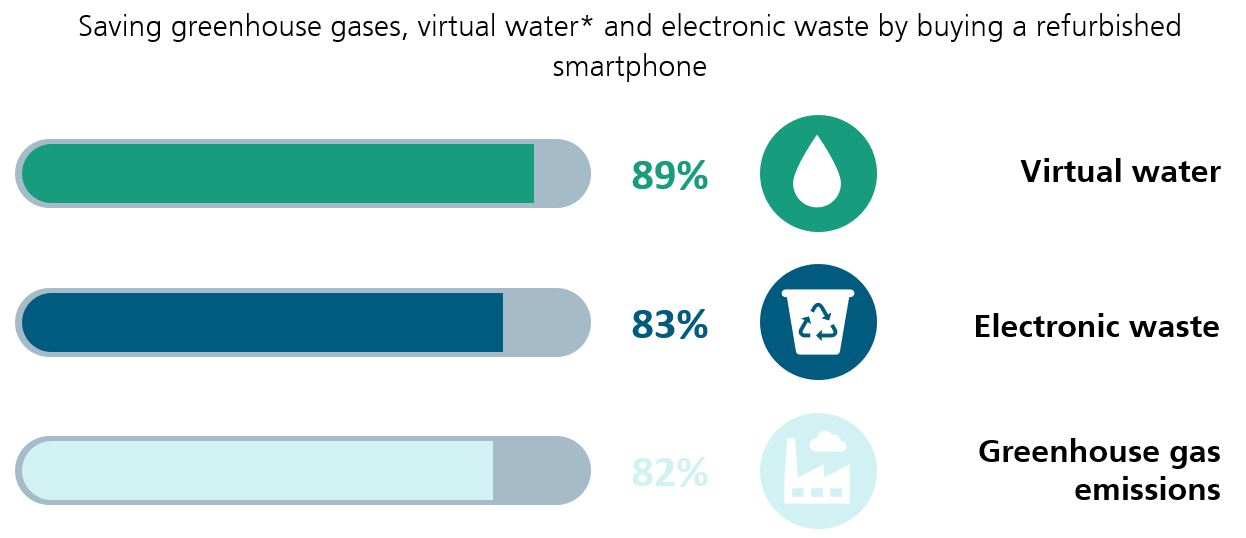
Savings when buying a used smartphone3:
What does the Green ICT @ FMD competence center do?
The aim is to use the structures created in the FMD (13 research institutes, including 11 Fraunhofer and 2 Leibniz) for application-oriented microelectronics research to support an expansion in terms of resource conservation and reduction of the carbon footprint in the further development of ICT applications and ICT infrastructure.
Three core technology projects, the Green ICT Hubs, are researching and working on making ICT greener:
- Hub 1: Sensor edge cloud systems
- Hub 2: Energy-saving communication infrastructures
- Hub 3: Resource-optimized electronics production
You want to delve deeper into the subject?
- 1) DNP: Nanoimprint lithography accelerating carbon neutrality in semiconductor production
https://www.global.dnp/media/detail/20167700_4104.html; 2)IEEE Spectrum (Jan. 2022): Scarcity Drives Fabs to Wastewater Recycling Boosting water recycling at fabs by up to 98 percent keeps chip production on target https://spectrum.ieee.org/fabs-cut-back-
water-use; 3) Semiconductor Digest: Water Supply Challenges for the Semiconductor Industry https://www.semi-
conductor-digest.com/water-supply-challenges-for-the-semiconductor-industry/; 4) Industry Today (Jan. 2022): Water’s Critical Role In Semiconductor Manufacturing https://industrytoday.com/waters-critical-role-in-semiconductor-manufacturing/; 5) TSMC TCFD report 2023 via Statista: Annual water consumption of Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) https://www.statista.com/statistics/1313040/tsmc-water-consumption-by-user/; 6) BCG: For Chip Makers, the Decarbonization Challenge Lies Upstream https://www.bcg.com/publications/2023/why-chip-makers-need-to-focus-on-the-upcoming-decarbonization-challenges ↩︎ - Rudorf, P. & Henjes, J. (2024). Ökobilanzierung von aufbereiteter Elektronik des Online-Marktplatzes der Refurbed Marketplace GmbH gemäß ISO 14040/44. Verfügbar unter: https://pub.refurbed.com/Sustainabilitypage/%C3%96kobilanzierungAufbereiteteElektronikger%C3%A4teRefurbed.pdf ↩︎
- Rudorf, P. & Henjes, J. (2024). Ermittlungsmethodik für ökologische Kennzahlen aufbereiteter Elektronik des Online-Marktplatzes der Refurbed Marketplace GmbH. Verfügbar unter: https://pub.refurbed.com/Sustainabilitypage/ErmittlungsmethodikAufbereiteteElektronikger%C3%A4teRefurbed.pdf ↩︎